Intelligent hardware is a technological concept following the smart phone. It combines the hardware and software to transform the traditional device, so that it has intelligent functions. After the intelligentization, the hardware has the ability to connect, realize the loading of Internet services, form a typical structure of “cloud+endâ€, and have added value such as big data. Smart hardware is a technology concept that refers to the intelligent transformation of traditional devices by combining hardware and software. The intelligent hardware mobile application is software. The application is connected with intelligent hardware, the operation is simple, the development is simple, and various applications are emerging one after another, which is also an important entry for enterprises to acquire users. The object of modification may be electronic devices such as watches, televisions, and other appliances; or devices that were not previously electronic, such as door locks, teacups, cars, and even houses. Intelligent hardware has extended from wearable devices to smart TVs, smart homes, smart cars, medical health, smart toys, robots and more. Typical intelligent hardware includes Google Glass, Samsung Gear, FitBit, Maikai Cup, Handcuffs, Tesla, LeTV and so on. At present, IoT technology is still in its infancy, and security has not been fully understood and clearly defined compared with other industries such as finance and e-commerce. When developing an IoT product, whether it's a small product like a wearable device or a large IoT deployment like an oilfield sensor network or a global distribution job, security issues must be considered from the start. To understand the security problem, you need to understand the attack method of the IoT device and improve the defense capabilities of the IoT product by studying the attack method. As the earliest team engaged in intelligent hardware security attack and defense research, based on the long-term intelligent hardware security attack and defense practice, the 360 ​​attack and defense laboratory systematically analyzes and combs the security risks of intelligent hardware devices, and summarizes the eight security risks of intelligent hardware devices. . The following content has been included in the forthcoming book "Intelligent Hardware Security", which will be the first professional book to introduce the security of the Internet of Things in China. The core point of the book is to "promote and prevent attacks". The safety concept fully enhances the security defense capabilities of the IoT products themselves. The following are eight security risks of intelligent hardware devices: Proportion of major security issues in intelligent hardware 1. Data storage is not secure There is no doubt that the biggest risk facing mobile device users is the loss or theft of devices. Anyone who picks up or steals the device can get the information stored on the device. This largely depends on what kind of protection the application on the device provides for the stored data. Many developers of smart hardware mobile phone clients do not choose reliable storage methods for intelligent hardware configuration information and control information. It can be read directly to the plaintext through the debug interface or directly to the logcat. User identity authentication credentials, session tokens, etc., can be securely stored in the trust domain of the device, and the hijacking control can be achieved by cracking the mobile device. 2. Server control measures are improperly deployed The security strategy of the existing intelligent hardware is to reduce the performance loss to the server. In many cases, the security rules are deployed on the client, and the input of all the input data of the client is not checked and standardized. Use regular expressions and other mechanisms to ensure that only allowed data can enter the client application. At the time of design, a set of common security requirements for the mobile terminal and the server are not implemented. The data parameters can be directly submitted to the cloud, and the client APK restricts the parameter filtering to achieve the purpose of cracking the device function. 3. No encryption during transmission In the process of using intelligent hardware, there is a case of connecting an open Wi-Fi network, so the protection measures in this scenario should be designed. We make a list to ensure that all application data in the list is protected during transmission (protection to ensure confidentiality and integrity). The list should include the authentication token, session token, and application data. Make sure to use SSL/TLS encryption when transmitting and receiving all inventory data (See CF Network Programming Guide). Make sure your application only accepts validated SSL certificates (CA chain verification is disabled in the test environment; make sure your application has removed such test code before it is released). Dynamic testing is used to verify that all inventory data is fully protected in the operation of the application. Through dynamic testing, ensure that certificates generated by forgery, self-signing, etc. are not accepted by the application under any circumstances, as shown in the following figure. The transmission process is not encrypted (the right side of the figure is the format of the plaintext data encoding) 4. Mobile client injection Input validation and output filtering for mobile client and web applications should follow the same rules. To standardize conversions and actively verify all input data. Parametric queries are used even for local SQLite/SQLcipher query calls. When using a URL scheme, pay special attention to verifying and receiving input, because any application on the device can call the URL scheme. When developing a web/mobile hybrid application, ensure that local/local permissions are the minimum permissions that meet its operational requirements. There is also the ability to control the content and pages of all UIWebViews to prevent users from accessing arbitrary, untrusted web content. 5. Improper authentication measures Most of the authorization and identity authentication are controlled by the server. The server will have security problems such as simple user security check, device ID rule, and poor authorization between devices. At present, in the case of analyzing the law of device identity authentication and identification, such as MAC address and SN number, it can be obtained by guessing and enumerating, thereby controlling a large number of devices in batches, as shown in the following figure. The vulnerability of this vulnerability is greatest in intelligent hardware because it affects all of the smart hardware. Improper authentication measures 6. Improper key protection measures Some IoT products have been designed with security encryption in mind, such as using AES 128-bit encryption for transport-encrypted content and MD5 for encrypting user passwords. In the process of symmetric encryption, the way the key is stored is crucial. In the IoT solution, the request initiated by the mobile client needs to encrypt the data content, that is, the AES key is required in the mobile client. If the key is stored improperly, it is easy to restore the data to plaintext for reverse analysis, so as to carry out further attacks. After conducting security research on a large number of IoT devices, it was found that the device basically stored the AES key in the mobile client, and some of them were very simple and written in an encryption function. Some are done very deeply and are placed in a Lib library. But these are just a certain technical threshold, not a solution to the security problem, as shown below. Improper password protection 7. The session is not handled properly There are a lot of smart devices that can be controlled by session hijacking attacks and directly control devices to achieve a degree of device cracking. Therefore, never use device unique identifiers (such as UDID, IP, MAC address, IEME). ) to mark a conversation. Guaranteed tokens can be quickly reset when the device is lost/stolen and the session is intercepted. Be sure to protect the confidentiality and integrity of the authentication token (for example, only use SSL/TLS to transfer data). Use a trusted service to generate a session. 8. Sensitive data leaks For the security research of smart devices, the data leaked out by the smart device can be further utilized to obtain control authority. So you must ensure that security is not on the mobile device; it is best to store them (such as algorithms, proprietary / confidential information) on the server side. If the security information must be stored on the mobile device, try to save them in the process memory. If you must put it on the device storage, you need to protect it. Do not hard code or simply store confidential data such as passwords and session tokens. Before publishing, clean up the sensitive information compiled into the binary data, because the compiled executable file can still be reversed. Sensitive data leak Dongguan Yijia Optoelectronics Co., Ltd. , http://www.everbestlcdlcm.com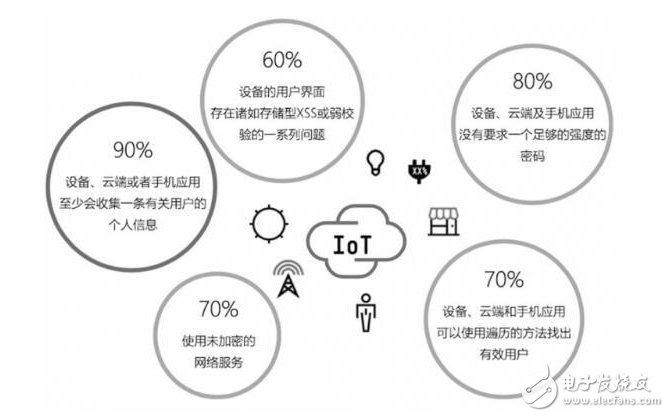




Analysis of eight hidden dangers of intelligent hardware devices
Intelligent hardware