WSN is actually a distributed sensor network. It is a sensor that can sense the outside and check the external world. It is the key technology of the Internet of Things. In the wireless sensor network, the positioning technology is a widely used important technology. In the distance-based positioning technology, the ranging accuracy largely determines the positioning accuracy. The traditional RSSI ranging method has many problems such as complex path loss model, serious fluctuation of the signal caused by environmental changes, and ranging error. Aiming at the above problems, this paper proposes an RSSI ranging method using the attenuation factor of the anchor node ranging signal. The distance measurement method does not need to establish a path loss model. At the same time, the signal attenuation factor has a strong correlation with the RSSI ranging, which reduces the other The ranging error caused by the signal intensity value caused by the factor has a good environment adaptability. Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) is a modern wireless detection area network with a large number of micro sensor nodes deployed. In the actual engineering application of wireless sensor networks, nodes need to provide their own location information and detection information in order to provide effective monitoring services [2-3]. Location, tracking, and trajectory prediction of targets in a wireless sensor network require location information of the nodes. The location problem of the WSN generally refers to a network node for a group of unknown location information, relying on the location information of the known anchor node, by measuring the distance or hop count of the unknown node to the remaining nodes, or by estimating the range of regions in which the node may be located, The information exchanged between nodes and the known location of the anchor nodes determine the location of each node [5]. The ranging method based on the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) means that the signal is reflected, refracted and absorbed when it encounters an obstacle during the propagation process, and the signal around the obstacle is relatively large. The path loss causes inaccuracy in ranging, and the maximum ranging error can reach ±50% [2]. In view of the shortcomings in the RSSI ranging method, this paper proposes an RSSI ranging method using the anchor node ranging signal to solve the ranging error. 1 node positioning technology basic theory 1.1 Range-Based positioning In Range-Based positioning, the accuracy of ranging between nodes determines the accuracy of positioning, and introduces the following common ranging methods. The TIme of Arrival (TOA) ranging method is a directional link-based positioning method that determines the position of a node by measuring the propagation time of the node signal to multiple beacon nodes. However, it does not deal with the same error of all nodes, and the error is large. The TIme Different of Arrival (TDOA) ranging method is another reverse link-based positioning method that determines the position of a node by detecting the time difference between arrivals of different signals. However, since the node power control causes the power received by the adjacent nodes to be small, a large measurement error is caused. Angle of arrival (AOA) positioning is estimated by two or more anchor nodes by measuring the angle of arrival of the received signal. When the node is far away from the coordinator, a slight deviation of the node positioning angle will result in a large error in the distance of the measuring line. The Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI) ranging method measures the received power through the receiving node, calculates the propagation loss, and converts the propagation loss into a distance using a theoretical or empirical signal path loss model. It does not need to add any additional hardware to reduce the input cost, but its path loss model is complicated to build. The RF signal is susceptible to multipath fading, non-line of sight and other environmental influences, causing the received signal strength value to be severely oscillated, making it difficult to accurately measure the distance. 1.2 Main factors affecting positioning accuracy Since the communication environment of wireless sensor networks is complex and variable, various positioning technologies that rely on communication signal measurement are affected by various factors, such as multipath propagation problems and NLOS propagation. 2 RSSI ranging method In the algorithm of the RSSI ranging method, the accuracy of the positioning is determined by the accuracy of the distance measurement between the known nodes. The basic idea of ​​the RSSI ranging method is: in the process of propagation, due to the attenuation of the signal, the signal propagation path loss model in a specific environment is applied to the desired signal propagation environment to calculate the signal between the nodes corresponding to the signal attenuation. Transmission distance. 2.1 RSSI ranging principle In the positioning algorithm of RSSI, the propagating signal propagates in free space, and its energy has no dielectric loss. The propagation path loss refers to the transmitting signal of the transmitting node in free space during the propagation process. As the distance increases, the signal is reflected and absorbed. The power density of the signal received by the node is reduced, the propagation loss of the signal is calculated, and the path loss model is established to convert the transmission loss amount into a corresponding distance [2-3, 6]. Path loss is a quadratic function of distance, and the expression is as follows: In the above formula, Pt is the node transmit power, Pt(d) is the received power; Gr and Gt are the gains of the transmit and receive antennas respectively; d is the distance from the transmitting node to the receiving node; n is the average path loss index depending on the environment. ; λ is the wavelength. Available from (1): Thus, the received signal power variation is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the transmitting node and the receiving node, and the distance between the transmitting and receiving nodes can be calculated by measuring the strength of the received signal using equation (2). 2.2 Advantages and Disadvantages of RSSI Ranging Method and Error Analysis However, in actual use, the RSSI ranging method is prone to multipath propagation, reflection, antenna gain, and non-line of sight due to environmental factors. Even in wireless sensor networks that are placed in fixed locations, when the environmental factors change, the signal attenuation rate is also It will change, causing the same distance to produce propagation loss of different environmental average path loss index, so the RSSI positioning technology is usually roughly positioned in the range-based positioning technology. 3 RSSI ranging method based on ranging signal 3.1 Improvement ideas For the signal propagation path loss in the RSSI ranging method, the attenuation factor of the anchor node ranging signal is proposed to be improved. The basic idea is to calculate the signal attenuation factor by means of the signal propagation loss between the two anchor nodes, and then use the signal attenuation factor for the ranging between the known node and the unknown node to calculate the distance. The routing layout idea is shown in Figure 1. Two-node location information is known in the wireless sensor network, and N2 is the required node. When N0 and N2 are in the same environment, the two nodes can communicate. The distance information of the known nodes N0 to N2 is used to measure the distance from N0 to N2, and the positioning information of the node N2 is determined. Using the idea of ​​anchor node attenuation signal attenuation factor, if there is an anchor node N1 in the communication range of node N0, then N0, N1, N2 are neighbor nodes, and there is no law in the ambient noise coefficient caused by the environmental noise coefficient in the small range of node N0 communication. The attenuation of the ambient noise factor has the same effect on the quality of signal communication between N0 to N2 and N0 to N1. In the same state, the attenuation of the signal from N0 to N2 is consistent with that from N0 to N1. Therefore, the numerical relationship between the signal attenuation rate and the distance in the same state is obtained by the anchor nodes N1 and N0, and the distance from N0 to N2 is calculated by the attenuation factor. In this improvement, the signal attenuation factor is derived by combining the signal with the increase of the distance and the attenuation. In the positioning process based on the RSSI ranging method, at least three anchor nodes need to be located in the communication range of the unknown node, so these anchor nodes can be utilized when calculating the attenuation factor, and no additional nodes are needed. 3.2 Signal random attenuation coefficient In the same environment, there are two anchor nodes N0, N1 and an unknown node N2, N0 and N1 and N0 and N2 can communicate with each other. The spacing between N0 and N1 is d1, and the signal strength of N0 is known to be PN0. When transmitting to N1, the signal strength is reduced to PN1; when transmitting from N0 to N2, the signal strength is reduced to PN2. The distance d from N0 to N2 needs to be measured (the schematic diagram is shown in Figure 2). The deduction is as follows: The relationship between the energy loss E of the signal transmitted by the wireless sensor network and the distance d: It can be seen that the RSSI ranging method based on the random attenuation coefficient of the anchor node assisted ranging signal utilizes the anchor node to assist the positioning. The ranging method does not need to establish a complex path loss model, but uses an anchor node auxiliary signal attenuation factor for ranging. 4 algorithm simulation analysis In order to test the performance of the RSSI ranging algorithm based on the anchor node auxiliary signal, the data collection is performed on the WSN algorithm on the NS2 platform, and the algorithm is analyzed by the simulation angle, that is, the PN2 is obtained when the PN0, PN1, and d1 take a certain value. The relationship with d. algorithm Figure 3 shows the effect of different environmental attenuation factors on the improved RSSI curve at fixed node N0 and node N2. It can be seen that the environmental attenuation factor n has a great influence on the propagation model. The smaller the n value is, the smoother the corresponding improved RSSI curve is, the slower the node signal is attenuated, and the smaller the node N2 positioning error is. Conversely, the larger the value of n, the faster the signal is attenuated and the larger the positioning error. Now give a set of values: The curve in the simulation diagram shows the relationship between the received signal strength and the distance of the node N2 obtained by the signal attenuation factor method. The signal intensity decays faster with the increase of the distance, and the attenuation speed is more uniform, and no signal intensity oscillation occurs. 5 Conclusion In the distance-based positioning technique, the positioning accuracy depends on the ranging accuracy. In this paper, the idea and method of using the attenuation factor of the anchor node ranging signal are proposed, and the principle of ranging is expounded, and the signal attenuation factor is derived. Compared with the traditional RSSI ranging method, the ranging method does not need to establish a complex path loss model, but calculates the simultaneous signal attenuation factor for ranging. The attenuation factor is now available to effectively reduce the signal caused by other factors. The ranging error caused by the intensity oscillation improves the positioning accuracy of the RSSI in the wireless sensor network.
Networking Keystone Jacks, Punch Down Type Terminals.China Network & Accessories,Networking KEYSTONE Jacks supplier & manufacturer, offer low price, high quality Punch Down Type Terminals,, etc.
Networking KEYSTONE Jacks, Punch Down Type Terminals.China Network & Accessories,Networking KEYSTONE Jacks supplier & manufacturer, offer low price, high quality Punch Down Type Terminals,, etc.
Networking KEYSTONE Jacks, Punch Down Type Terminals.China Network & Accessories,Networking KEYSTONE Jacks supplier & manufacturer, offer low price, high quality Punch Down Type Terminals,, etc. Network & Accessories,Networking KEYSTONE Jacks, Punch Down Type Terminals ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenkconn.com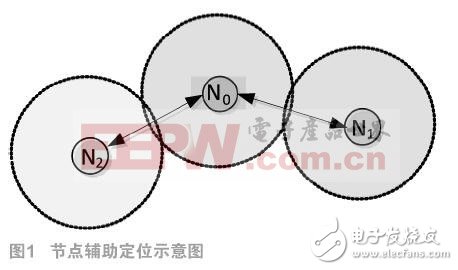
![]() (1)
(1) 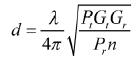 (2)
(2) 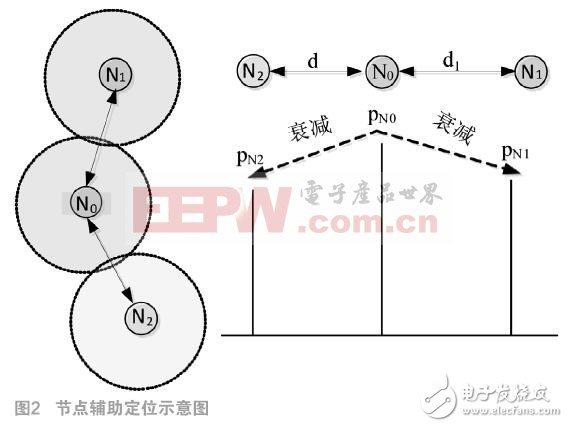

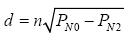 ,among them,
,among them, 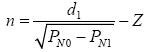 It is the signal attenuation factor, which is obtained by two anchor nodes N0, N1. When the environment changes, n changes accordingly.
It is the signal attenuation factor, which is obtained by two anchor nodes N0, N1. When the environment changes, n changes accordingly. 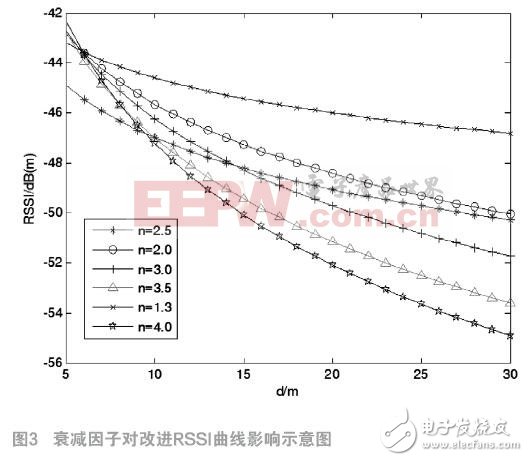
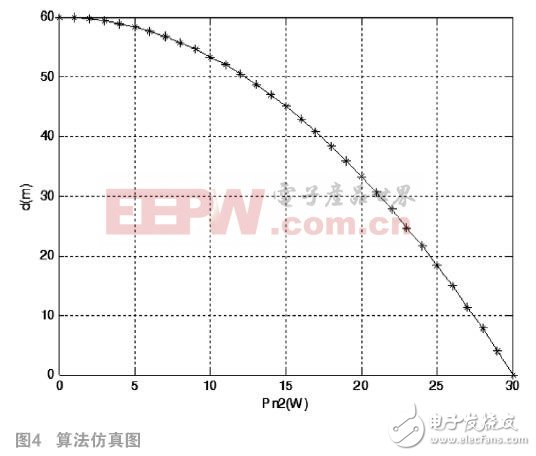
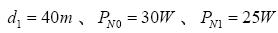 , when
, when 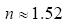 At the time, Matlab2016a through the algorithm simulation analysis, draw a relationship between d and PN2, as shown in Figure 4.
At the time, Matlab2016a through the algorithm simulation analysis, draw a relationship between d and PN2, as shown in Figure 4.