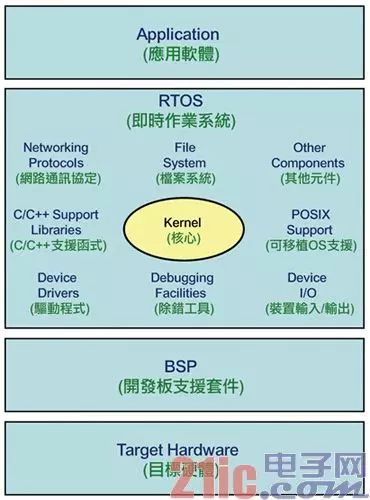
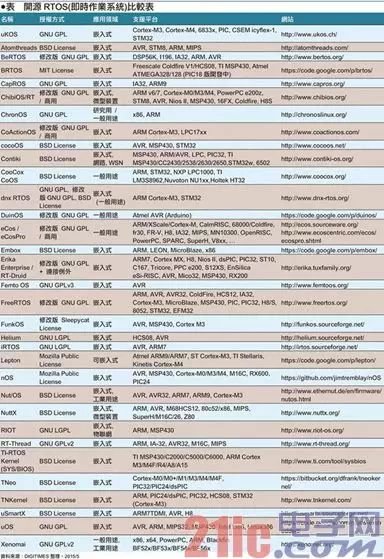
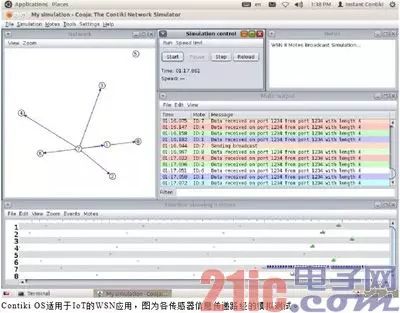
Microcontrollers (MCUs) are widely used in various industries, such as various types of home appliances, industrial automation, real-time control, and data acquisition. In order to meet the needs of real-time control and rapid response required for industrial control, most MCUs are equipped with MCUs. RTOS (real-time operating system) operation. With the rise of the Internet of Things, the software industry has also added components of the Internet of Things for RTOS to advance the core software market for IoT... Various processor-specific OS In the general-purpose processor market category, the functions and execution speeds are broadly classified into CPU> MPU> MCU. The CPU has the strongest functions and is mainly used in computer products; the MPU function is the second, and its applications are diverse, mainly used in embedded systems and thin computers; and MCUs are based on single applications and are applied to various types of household appliances. , electronic products, embedded products, wearable devices, Internet of Things (IoT) applications and other control applications. The MCU integrates a KHz-MHz class CPU, KB-MB class memory units (RAM and ROM/EEPROM/Flash), an oscillator generator (Clock Generator), and an I/O expansion unit. A slower system-on-a-chip (SoC). Due to the small internal memory capacity, large-scale operating systems such as Windows, Linux, etc. cannot be plugged into the MCU for execution, and MCUs are mostly used in real-time control environments, so many small-capacity RTOSs (Real-Time Operating System; real-time) The operating system) became the main platform for developing MCU software. Medium and high-level RTOS that focuses on embedded applications There are many types of RTOS, which are mainly designed for use in embedded systems based on MPU or MCU. For example, the MPU level dedicated to Integrity, QNX, VxWorks and other powerful RTOS; As for the smaller size, mainly to support the MCU-level RTOS, Nucleus, ThreadX, Unison OS, ucOS II / III and so on. For example, the Integrity OS introduced by Green Hills Software is an RTOS that supports MPU (even CPU level). Its strength lies in the Integrity-178 version has passed EAL 6+? (Information Security) certification and DO-178B (Flying Environment) A-level certification, is applied in markets that attach great importance to safety and reliability, such as fighter aircraft (such as B-2 , F-16, F-22, F-35) and civilian aircraft (such as Airbus A380) and other fields. The RTOS supports CPU/MPU platforms such as ARM, XScale, Blackfin, Freescale (incorporated into NXP) ColdFire, MIPS, PowerPC, AMD x86 (embedded APU). Another well-known QNX RTOS, using the micro-core architecture, is the only OS that has successfully entered the commercial market. Its strength is multimedia real-time processing capabilities. It is suitable for embedded markets such as entertainment devices and mobile phones on vehicles (machines). QNX was acquired by BlackBerry in 2010 and developed the BB 10 operating system. QNX supports CPU/MPU platforms such as IA32, MIPS, PowerPC, SH-4, ARM, StrongARM, and XScale. As for IntervalZero's RTX and RTX64, it is an RTOS designed to coexist and coexist with Microsoft Windows, with the EtherCAT protocol as a factory automation application. Among them, Windows is mainly responsible for GUI, storage, and computing. RTX is responsible for real-time industrial control and data collection, making it easier to develop industrial control software. The above RTOS is an MB-to-GB MPU-level OS and does not apply to the MCU environment. Commercial RTOS that focuses on MCU applications The middle and low-order RTOS part is mainly to simplify the software functions to MB or even KB level, so that the entire OS and main application programs can be plugged into the ROM/EEPROM/Flash in the MCU. Since the MCU application area is more extensive, its software must strive to be more streamlined. Therefore, MCU-dedicated RTOSs mostly have a very highly modular architecture. The core, driver, file system, peripheral I/O, and network support can all be measured. Tailored to facilitate rapid product availability. Some commercial RTOSs provide source code to authorized customers, while open source RTOSs are more freely usable, allowing developers to compile a minimal and optimized execution environment for code. Since the MCU products/development boards introduced by each chip factory will have their corresponding OS and IDE (integrated software development environment), these OS and software development environments may only be applicable to the MCU products of the plant, so third-party software vendors , To develop a cross-chip / cross-hardware platform OS and IDE, so that developers do not have to change the hardware platform, the software must be completely rewritten. At present, the market share of MCU OS/IDE is the highest. Most software companies launch commercial RTOS (along with MCU products from various vendors). However, as ARM introduces Cortex-M, Cortex-R and other instruction set architectures, it will enter into wearables and objects. The networking application market makes the RTOS of the ARM architecture (starting source code) begin to increase. Nucleus, introduced by Accelerated Technology of Mentor Graphics, adopts Microkernel design and claims to have 3 billion devices imported. The advantage is that the core length can be as small as 2KB, and developers do not need to write BSP for embedded devices (development board support package) Therefore, it is widely used in consumer electronics, mobile devices, automotive electronics, smart energy, medical equipment, industrial / industrial control and other fields. In the early days, Continental, White, and Dual SIM 2G mobile phones using MediaTek MT6217 chips were implementing Nucleus RTOS. The RTOS supports embedded MCU architectures such as ARM, MicroBlaze, MIPS, Nios II, Power, SuperH, and XScale. ThreadX, released by Express Logic, is a royalty-free RTOS. Its advantages are ultra-fast boot time and response time. Its Picokernel core is less than 2KB in length, and it claims to have 2.1 billion devices imported through security specifications. use. For example, HP's printers and peripherals use this RTOS. Can support a wide variety of 32-bit MCUs, including ARM, Atmel, BlackFin, CoreFire/68K, EFM32, Freescale (NXP), FM3, H8, XMC, M-Core, MicroBlaze, MIPS, Nios II, Power, STM32, StrongARM Synopsys ARC, TI, Win32, x86/x386, XScale, and more. Wind River's VxWorks is designed for embedded system design and adopts the monolithic core. The advantage is that it has preemptive multiprocessing cores, loop execution, and rapid response. It supports native 64-bit processing. The processor architecture (x64), parallel (SMP)/non-parallel (AMP) processing, has accumulated over 1.5 billion devices imported to date. The new version of VxWorks 7 targets the scalability, security, connectivity, drawing capabilities, virtualization, and other enhancements required by IoT, while the full-featured VxWorks microcore is only 20KB in length. VxWorks is widely adopted by the technology industry. VxWorks is used by Curiosity who lands on Mars. The RTOS supports CPU/MPU architectures such as Intel x86 (including Quark SoC and x86-64), MIPS, PowerPC, SH-4, and ARM. RoweBots' Unison OS is an RTOS fully compatible with POSIX (Portable Operating System Interface) and is suitable for 32-bit hardware development environments such as MCU, DSC, DSP, SoC, and FPGA. Networked applications enhance their system security, and core code can be as low as 1KB in some application architectures. Supports 32-bit MCUs such as the Microchip PIC32, Renesas R32C/SH2A, ST STM32, and TI ARM Cortex-M3. Micrium's μc/OS-II (microcontroller OS version 2), which features a portable, ROM-executable, flexible, preemptive RTOS core, can manage up to 250 application tasks. Μc/OS-III is the main application of unlimited application tasks, almost zero of the cut off, and can provide the source code to the customer. Its advantage is that the system's original code is open, clean and consistent, and the comments are exhaustive. It also passes FAA certification and DO-178B certification, and is suitable for various embedded and Internet of Things system development. The core size is from 5 or 6 KB to 24 KB. As for the μc/OS-III HW-RTOS, it is hardware acceleration for ARM Cortex-M-based MCUs. The RTOS supports more than 100 DSPs, MPUs, and MCUs. ARM MCU Boosts Open-Source RTOS In recent years, ARM-based processors have swept the global smart mobile device (mobile phone/tablet) market, in addition to the commercial RTOS/IDE introduced by each MCU/MPU hardware platform, to enter the IoT and wearable MCU-level applications, ARM introduced the instruction set architecture of Cortex-M and Cortex-R, and used open source OS/IDE to seize the MCU application market. For example, mbed OS and related development environment introduced by ARM focus on the application of embedded devices and IoT. OS with connectivity, high efficiency, security and productivity, together with its mbed-rtos library, can also be used as RTOS. Applications. The mbed development environment can develop applications such as smart homes, smart cities, and wearables. In addition, there are many open source RTOS/IDEs for ARM platforms such as FreeRTOS, uKOS-II, Atomthreads, BeRTOS Community Edition, ChibiOS/RT, CoActionOS, eCos, Embox, Erika Enterprise/RT-Druid, Keil (ARM) RTX, Lepton, nOS, Nut/OS, NuttX, RIOT, RT-Thread, TI-RTOS-KERNEL (SYS/BIOS), TNeo, and more give developers more choices. Non-real-time OS overview of other dedicated MCUs In addition, there are many open source OSs (non-RTOSs) that are designed for MCUs, but they also have small features, some of which are for WSN (Wireless Sensing Network) applications such as Contiki OS and TinyOS. Some have general desktop GUIs such as SymbOS and Wheels OS. Contiki OS is a set of open source micro OS that can be used in IoT applications such as Atmel ARM/AVR, LPC, PIC32, TI MSP430/CC2430/2538/2630/2650, STM32W and other MCUs. It can also be used as a museum-level 8-bit computer. (Apple II, Atari, Commodore, etc.) are connected to the Internet and even executed on the ashes (Atari Jaguar, Game Boy/Advance, GP32, Nintendo Red and White, PC Engine, etc.). As for SymbOS, it is a set of free multimedia graphic operating systems that can be executed on antique computers with 8-bit Z80 CPUs (such as MSX and Amstrad), giving Windows 95-like operation screens to rejuvenate old computers.
Ebang Ebit Mining Machine:Ebang Ebit E11++,Ebang Ebit E9,Ebang Ebit E9.2,Ebang Ebit E9+,Ebang Ebit E9i,Ebang Ebit E11+,bang Ebit E10,Ebang Ebit E11
Ebang is a blockchain production company specializing in the production of Bitcoin machines. Their ebit series has always been a cost-effective series of Bitcoin machines, with stable income, low machine loss and guaranteed after-sales service.
Ebang Ebit Mining Machine,E9 25Th/S Miner,ebit miner,ebit mining machine,ebang miner Shenzhen YLHM Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.sggminer.com