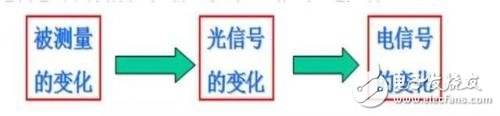
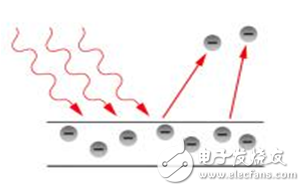
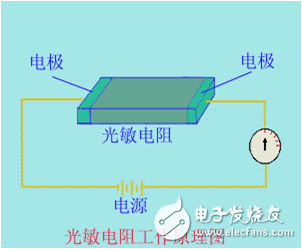
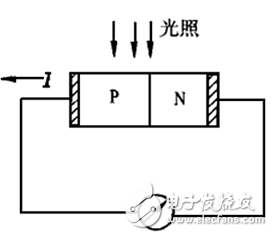
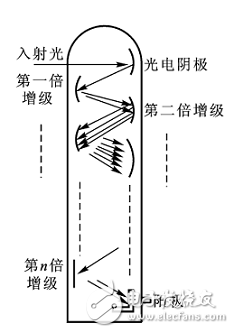
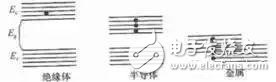
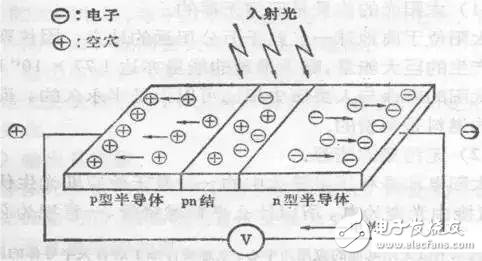
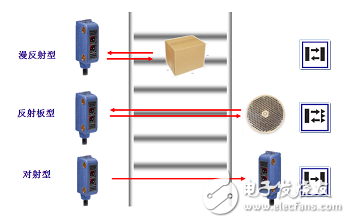
Photoelectric sensor is a kind of small electronic equipment, a key component of photoelectric conversion in various photoelectric detection systems. It is mainly a sensor that uses various properties of light to detect the presence or absence of objects and changes in surface conditions. Photoelectric sensors have the characteristics of non-contact, fast response, reliable performance, etc., so they are widely used in industrial automation devices and robots. The photoelectric sensor is generally composed of three parts: a light source, an optical path, and a photoelectric element. The measured change is converted into a change in an optical signal, and then the optical signal is further converted into an electrical signal with the help of a photoelectric element. The photoelectric element is the most important part of the photoelectric sensor, and its core working principle is different types of photoelectric effect. According to the wave-particle duality, light is composed of photons moving at the speed of light. When an object is illuminated by light, its internal electrons absorb the energy of the photon and change state, and its own electrical properties will also change. This phenomenon is called For the photoelectric effect. According to the different changes of electrical properties, the photoelectric effect is divided into the following three types: 1) External photoelectric effect The phenomenon that electrons escape from the surface of an object under the action of light is called the external photoelectric effect. Photoelectric components based on external photoelectric effect include phototubes, photomultiplier tubes, etc. 2) Photoconductive effect The phenomenon that the electrons in the semiconductor cannot jump out of the semiconductor after absorbing the photon, changes the conductivity of the object, or generates the photoelectromotive force, is called the internal photoelectric effect. The internal photoelectric effect can be divided into photoconductive effect and photovoltaic effect according to its working principle. Photoelectric components based on the photoconductive effect include photoresistors, phototransistors, etc. 3) Photovoltaic effect Under the action of light, the phenomenon that an object generates an electromotive force in a certain direction is called the photovoltaic effect. Photoelectric components based on the photovoltaic effect include photocells, photodiodes, triodes, etc. Based on different photoelectric effects, let’s take a look at how they work: Photoelectric devices made by using the external photoelectric effect of substances emitting electrons under the irradiation of light are generally vacuum or gas-filled photoelectric devices, such as photoelectric tubes and photomultiplier tubes. Taking a phototube as an example, when incident light is irradiated on the cathode, a single photon transfers all its energy to a free electron in the cathode material, thereby increasing the energy of the free electron. When the energy obtained by the electron is greater than the work function of the cathode material, it can overcome the bondage of the metal surface and escape to form electron emission. This type of electron is called a photoelectron. Only when the frequency of the incident light is higher than the limit frequency, photoelectrons will be produced. After the photoelectron is generated, it is absorbed by the anode in the vacuum tube, thereby generating an electric current. If the light intensity is increased at this time, more photons will irradiate the cathode material, thereby generating more photoelectrons, and the photocurrent will increase accordingly. When the resistance R value is determined, the photocurrent in the loop is a function of the light intensity of the incident light, thereby realizing photoelectric conversion. The light intensity can be calculated by reading the current through the measuring circuit. Photoelectric devices that use materials to change electrical conductivity or generate electromotive force under the irradiation of light are called internal photoelectric effect devices. The common ones are photoresistors, photocells, and phototransistors. According to energy band theory, the energy state of electrons in free atoms is not arbitrary, and electrons can only exist at a certain energy level. Energy band is divided into valence band, forbidden band and conduction band. Electrons can flow in the conduction band, but cannot flow in the valence band. Under external influence, electrons can enter the conduction band by crossing the band gap from the valence band, thereby changing the resistance of the conductor. The band gap thickness of different conductors is different. As shown in the figure below, the band gap of the insulator is wide, which makes it difficult for electrons to transition from the valence band to the conduction band, so its resistance is very large; the metal conductor has no band gap, and its valence band and conduction The belts are connected, so the conductivity is good. After the electron absorbs the photon energy, it transitions from the valence band to the conduction band to change the conductor resistance is called the internal photoelectric effect. This effect can be used to make photoresistors, and the amount of light to be measured can be determined by observing the changes in resistance. Photovoltaic effect is abbreviated as photovoltaic effect, which refers to the phenomenon that an object generates electromotive force after being exposed to light. Photocell is a kind of self-generating photoelectric element. It can generate electromotive force in a certain direction when it is exposed to light. Without Power Supply, as long as the external circuit is connected, current will flow. The specific working principle is as follows: In a photovoltaic cell, a large-area PN junction is formed by doping some P-type impurities on a piece of N-type silicon wafer by diffusion method. There are a lot of holes in the P area and a lot of electrons in the N area. When light irradiates the surface of the P zone, if the photon energy is greater than the band gap of silicon, each photon absorbed in the P-type zone will produce an electron-hole pair. The more photons absorbed on the surface of the P zone, the excited electrons will be empty. The more holes, the less the PN junction area is. Since the direction of the electric field in the PN junction points from the N area to the P area, it separates the electron-hole pairs that diffuse to the vicinity of the PN junction, the photogenerated electrons are pushed to the N area, and the photogenerated holes are left in the P area. So that the N zone is negatively charged, and the P zone is positively charged, forming a photoelectromotive force. If a wire is used to connect the P area and the N area, a photocurrent will flow in the circuit. According to the detection method, the photoelectric sensor is divided into diffuse reflection type, reflective plate type, and through-beam type: According to the corresponding detection methods, there are the following photoelectric sensors with different structures: ⑴ Slot-type photoelectric sensor A light emitter and a receiver are mounted face to face on both sides of a slot is a slot-shaped photoelectric. The illuminator can emit infrared light or visible light, and the light receiver can receive light without obstruction. But when the detected object passes through the slot, the light is blocked, and the photoelectric switch is activated. Output a switch control signal to cut off or switch on the load current to complete a control action. The detection distance of the slot switch is generally only a few centimeters due to the limitation of the overall structure. ⑵ Through-beam photoelectric sensor If the light-emitting device and the light-receiving device are separated, the detection distance can be increased. The photoelectric switch composed of a light emitter and a light receiver is called a through-beam separate photoelectric switch, or a through-beam photoelectric switch for short. Its detection distance can reach several meters or even tens of meters. When in use, the light emitter and the light receiver are respectively installed on both sides of the passing path of the detected object, and the light path is blocked when the detected object passes, and the light receiver acts to output a switch control signal. ⑶Reflective plate type photoelectric switch The light-emitting device and the light-receiving device are installed in the same device, a reflector is installed in front of it, and the photoelectric control function is completed by the principle of reflection, which is called the reflector reflection type (or mirror reflection type) photoelectric switch. Under normal circumstances, the light emitted by the light emitter is reflected by the reflector and received by the light receiver; once the light path is blocked by the detection object and the light receiver cannot receive light, the photoelectric switch will act and output a switch control signal. ⑷Diffuse reflection type photoelectric switch It also has a light-emitting device and a light-receiving device in its detection head, but there is no reflector in the front. Under normal circumstances, the light receiver from the illuminator cannot be found. When the detection object passes through and blocks the light and reflects part of the light back, the receiver receives the light signal and outputs a switch signal. The basic characteristics of the photoelectric sensor include the relationship curve between the output current and the voltage across the receiver, the relationship curve between the output current and the input current of the transmitter, the relationship curve between the output current and the temperature, and the pulse response characteristic curve. It has the following characteristics in industrial production applications: 1. Long detection distance If the detection distance of 10m or more is reserved in the through-beam type, it can be realized that other detection methods (magnetic, ultrasonic, etc.) cannot detect remotely. 2. Less restrictions on detecting objects As the detection principle is based on the shading and reflection caused by the detection object, it can detect almost all objects such as glass, plastic, wood, liquid, etc., unlike proximity sensors, etc., which limit the detection object to metal. 3. Short response time The light itself is high speed, and the circuit of the sensor is composed of electronic parts, so no mechanical working time is included, and the response time is very short. 4. High resolution High-resolution can be achieved by using advanced design technology to concentrate the projected light beam on a small spot, or by forming a special light-receiving optical system. It can also detect small objects and high-precision position detection. 5. Non-contact detection can be realized The detection can be achieved without mechanically touching the detection object, so it will not cause damage to the detection object and the sensor. Therefore, the sensor can be used for a long time. 6. Color discrimination can be realized The reflectance and absorptivity of the light formed by the detection object differ according to the combination of the wavelength of the light projected and the color of the detection object. Using this property, the color of the detected object can be detected. 7. Easy to adjust In the type of projected visible light, the projected light beam is visible to the eyes, which facilitates the adjustment of the position of the detection object. The following factors should be considered in the selection of photoelectric sensor before use: Detect object 1. Through-beam type (the size of the measured surface of the object) 2. Retro-reflective type (the size of the measured surface of the object, the strong or weak gloss reflection ability) 3. Diffuse reflection type (the size of the object being measured, the color of the object being measured) Detection method 1. Opposite beam type (projector + receiver), 2. Retro-reflective type (reflector+projector and receiver), 3. Diffuse reflection type (rely on the object to reflect the emitted light back to the light receiver, it is necessary to confirm whether there is a background object) Output form 1. Normally open (NO) 2. Normally closed (NC) 3. Normally open (NO) + Normally closed (NC) 4. Normally open (NO) or Normally closed (NC) Detection distance 1. Through-beam type (distance from emitter to receiver), 2. Retro-reflective type (the distance between the reflector and the receiver), 3. Diffuse reflection type (the distance from the measured object to the light emitting and receiving device) Control output 1. Transistor output (NPN low-level output, PNP high-level output) 2. Relay contact output Power supply 1. DC 2. Communication 3. Universal AC and DC Installation connection method 1. Wire lead type (default wire length is 1.2m) 2. Connector type (the straightness or L-shape of the patch cord needs to be confirmed, and the length of the wire) Other functions Delay function (E3JM) annex Reflector, installation accessories (for fixed installation of sensors) With the continuous improvement of the degree of automated production, the requirements for sensors are also constantly improving, which has prompted the photoelectric sensor to have to be updated with the pace of the times. The improvement of the performance of the photoelectric sensor must move towards high sensitivity, high accuracy, fast response speed, and mutual Change the direction of development.
The Asus range of laptops is targeted towards the retail end-user market
and hence the demand for the full range of Asus Laptop Charger is very high.
Asus
laptop charger include Asus VivoBook charger series, ASUS Zenbook charger series,
Transforme Book charger series and so on. If you want to find a replacement power Adapter for Asus laptop,
please feel free to contact us, we will help to select the correct OEM
replacement Asus
laptop adapter for you.
The common Asus laptop charger specifications have 12V 3A 44W,
19V 1.75A 33W, 19V 2.37A 45W 19V 3.42A 65W, 19V 4.74A 90W etc, and the dc tip
has 4.8*1.7mm, 4.0*1.35mm, 3.0*1.1mm, and special USB 6 pin, 40pin etc. Also
Yidashun can produce 45W 5V/12V 2A 20V 2.25A type c adapter for Asus
Yidashun's laptop adapter is with smart IC to protect your
laptop with over current protection, over load protection, short circuit
protection, over heat protection. And all our Asus laptop adapter is Brand New Replacement Product, works as Genuine parts, 100% OEM Compatible!!
Asus Laptop Charger,Asus Charger,Asus Computer Charger,Asus Notebook PC Charger Shenzhen Yidashun Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ydsadapter.com