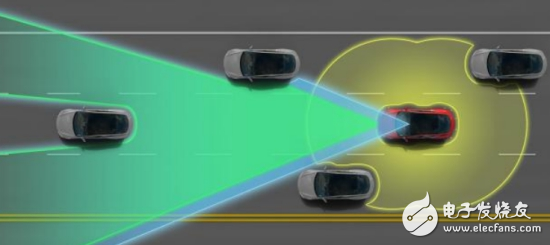
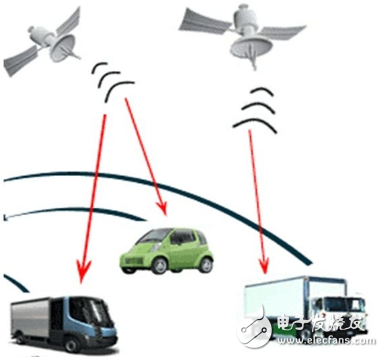
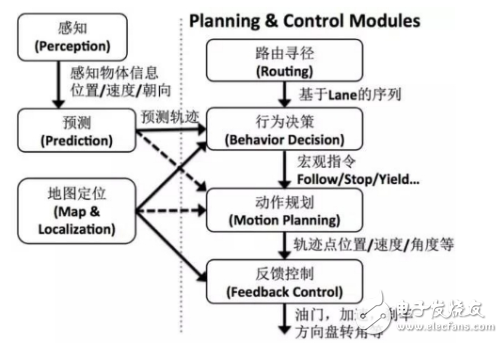
Driverless technology is a combination of sensors, computers, artificial intelligence, communication, navigation and positioning, pattern recognition, machine vision, intelligent control and many other frontier disciplines. According to the functional modules of driverless cars, the key technologies of driverless vehicles include environmental awareness, navigation and positioning, path planning, and decision control. (1) Environmental awareness technology The environment-aware module is equivalent to the eyes and ears of a driverless car, and the driverless car uses the environment-aware module to distinguish environmental information around itself. Provide information support for their behavioral decisions. Environmental perception includes the two parts of the driver's own position perception and surrounding environment perception. A single sensor can only measure a certain aspect or a certain feature of the measured object, and cannot meet the measurement needs. Therefore, it is necessary to simultaneously measure one or several feature quantities of a certain object to be measured by using a plurality of sensors, and the measured data is subjected to data fusion processing. Extract useful signals with high reliability. According to the different objects of the environment-aware system, we use two methods to detect: the position information of the driver's own car mainly includes the speed, acceleration, inclination, position and other information of the vehicle itself. This type of information is easy to measure, and is mainly measured by sensors such as a drive motor, an electronic compass, a tilt sensor, and a gyroscope. The surrounding environment of the driverless car is mainly based on active ranging sensors such as radar, and the passive range measuring sensor is supplemented by information fusion method. Because the combination of active range sensors such as laser, radar and ultrasonic can meet the needs of complex and harsh conditions and perform tasks, the most important thing is to process small amount of data and good real-time performance. At the same time, when planning the path, the data returned by the laser can be directly used for calculation, without knowing the specific information of the obstacle. Vision is an important means of environmental perception, although there are certain problems in the perception of harsh environments. However, in terms of target recognition, road tracking, map creation, etc., it has the importance that other sensors cannot replace. In the field of plant classification, water and mud detection in the wild environment, vision is also an indispensable means. (2) Navigation and positioning technology The navigation module of the driverless car is used to determine the geographical location of the driverless car, which is the support for the path planning and mission planning of the driverless car. Navigation can be divided into autonomous navigation and network navigation. The autonomous navigation technology means that in addition to the positioning assistance, the navigation task can be completed independently without the need of other external assistance. Autonomous navigation technology stores geospatial data locally. All calculations are done at the terminal, and positioning can be achieved under any circumstances. However, the computational resources of autonomous navigation devices are limited, resulting in poor computing power and sometimes unable to provide accurate and real-time navigation services. Existing autonomous navigation technologies can be divided into three categories: Relative positioning: mainly rely on internal feel sensors such as odometers and gyroscopes to determine the current position of the unmanned vehicle by measuring the displacement of the unmanned vehicle relative to the initial position. Absolute positioning: mainly using navigation beacons. Active or passive tying map matching or global positioning system for positioning. Combined positioning: comprehensively adopting the methods of relative positioning and absolute positioning to make up for the shortcomings and make up for the shortcomings of the single positioning method. The combined positioning scheme generally has GPs+map matching, GPs+track estimation, GPs+track estimation+map matching, GPs+GLONAss+inertial navigation+map matching. Network navigation can exchange information through wireless communication networks and traffic information centers anytime and anywhere. The mobile device is connected to a web GIs server directly connected to the Internet through a mobile communication network, and performs functions such as map storage and complex calculation on the server, and the user can download map data from the server. The advantage of network navigation is that there is no limitation on storage capacity and strong computing power. Ability to store any fine map, and the map data is always up to date. (3) Path planning technology Path planning is a bridge between information perception and intelligent control of driverless vehicles, and is the basis for autonomous driving. The task of path planning is to find a collision-free path from the initial state, including position and attitude, to the target state according to certain evaluation criteria in an environment with obstacles. Path planning techniques can be divided into global path planning and partial path planning. Global path planning is the use of known local information, such as obstacle locations and road boundaries, to determine feasible and optimal paths in the case of known maps. It combines optimization and feedback mechanisms. The local path planning is to guide the trajectory of the current front section of the unmanned platform according to the local environmental information sensed by the sensor under the guidance of the travelable area generated by the global path planning. Global path planning is for situations known to the surrounding environment, and local path planning is applicable to situations where the environment is unknown. Path planning algorithms include viewable method, grid method, artificial potential field method, probability road sign method, random search tree algorithm, particle swarm algorithm and so on. (4) Decision Control Technology The decision control module is equivalent to the brain of a driverless car. Its main function is to make decision decisions based on the information acquired by the sensing system, and then make decisions on the next behavior, and then control the vehicle. Decision-making techniques mainly include techniques such as fuzzy reasoning, reinforcement learning, neural networks, and Bayesian networks. The behavior of the decision control system is divided into three types: reactive, reflective and integrated: reactive control is a feedback control process that continuously adjusts the steering wheel angle and speed according to the deviation between the current position of the vehicle and the desired path until it reaches destination. LED Flexible Light Strip Kindwin Technology (H.K.) Limited , https://www.szktlled.com